The Hippo Pathway Core Cassette Regulates Asymmetric Cell Division
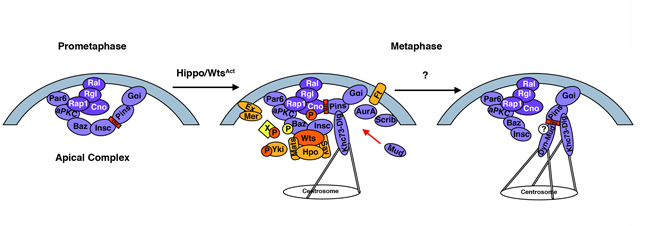
Asymmetric cell division (ACD) is a crucial process during development, homeostasis, and cancer. Stem and progenitor cells divide asymmetrically, giving rise to two daughter cells, one of which retains the parent cell self-renewal capacity, while the other is committed to differentiation. Any imbalance in this process can induce overgrowth or even a cancer-like state. Here, we show that core components of the Hippo signaling pathway, an evolutionarily conserved organ growth regulator, modulate ACD in Drosophila. Hippo pathway inactivation disrupts the asymmetric localization of ACD regulators, leading to aberrant mitotic spindle orientation and defects in the generation of unequal-sized daughter cells. The Hippo pathway downstream kinase Warts, LATS1-2 in mammals, associates with the ACD modulators Inscuteable and Bazooka in vivo and phosphorylates Canoe, the ortholog of Afadin/AF-6, in vitro. Moreover, phosphosite mutant Canoe protein fails to form apical crescents in dividing neuroblasts in vivo, and the lack of Canoe phosphorylation by Warts leads to failures of Discs Large apical localization in metaphase neuroblasts. Given the relevance of ACD in stem cells during tissue homeostasis, and the well-documented role of the Hippo pathway as a tumor suppressor, these results represent a potential route for perturbations in the Hippo signaling to induce tumorigenesis via aberrant stem cell divisions.

 English
English