Glial-secreted Netrins regulate Robo1/Rac1-Cdc42 signaling threshold levels during Drosophila asymmetric neural stem and progenitor cell division.
SUMMARY
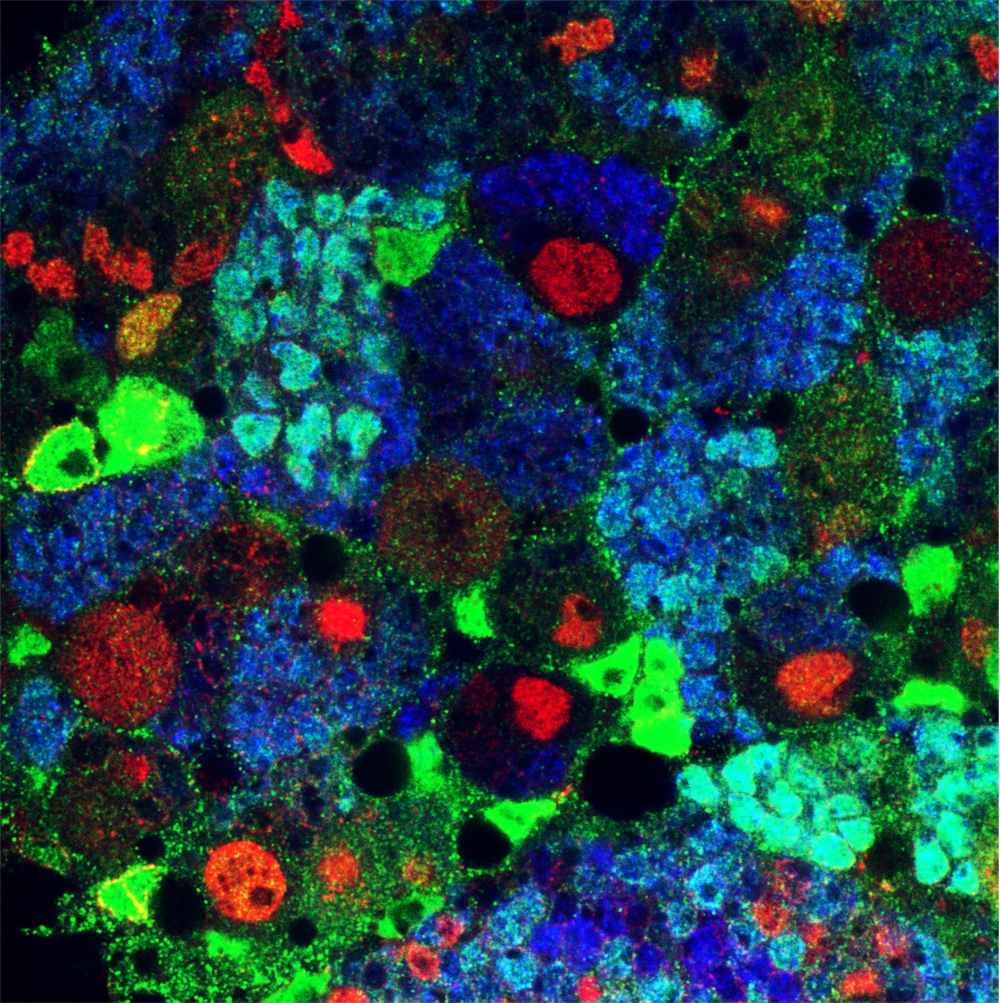
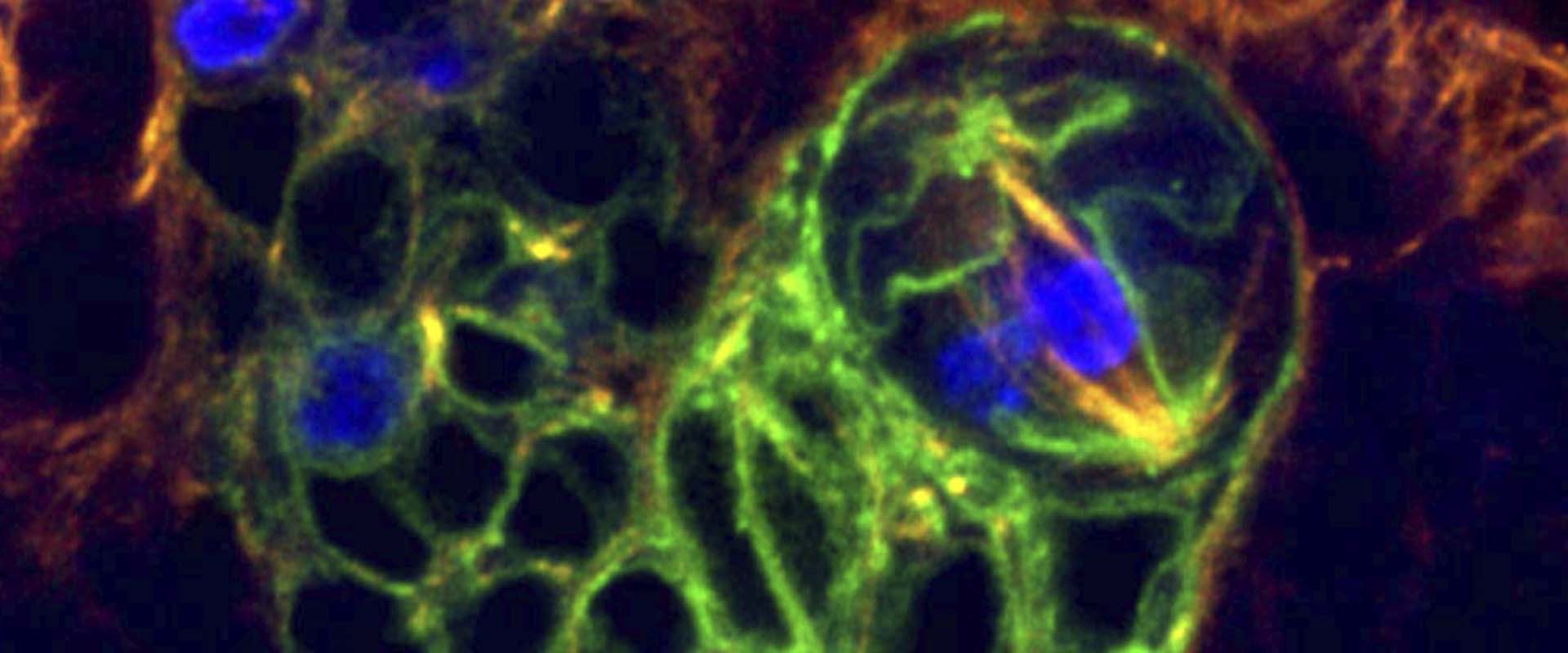
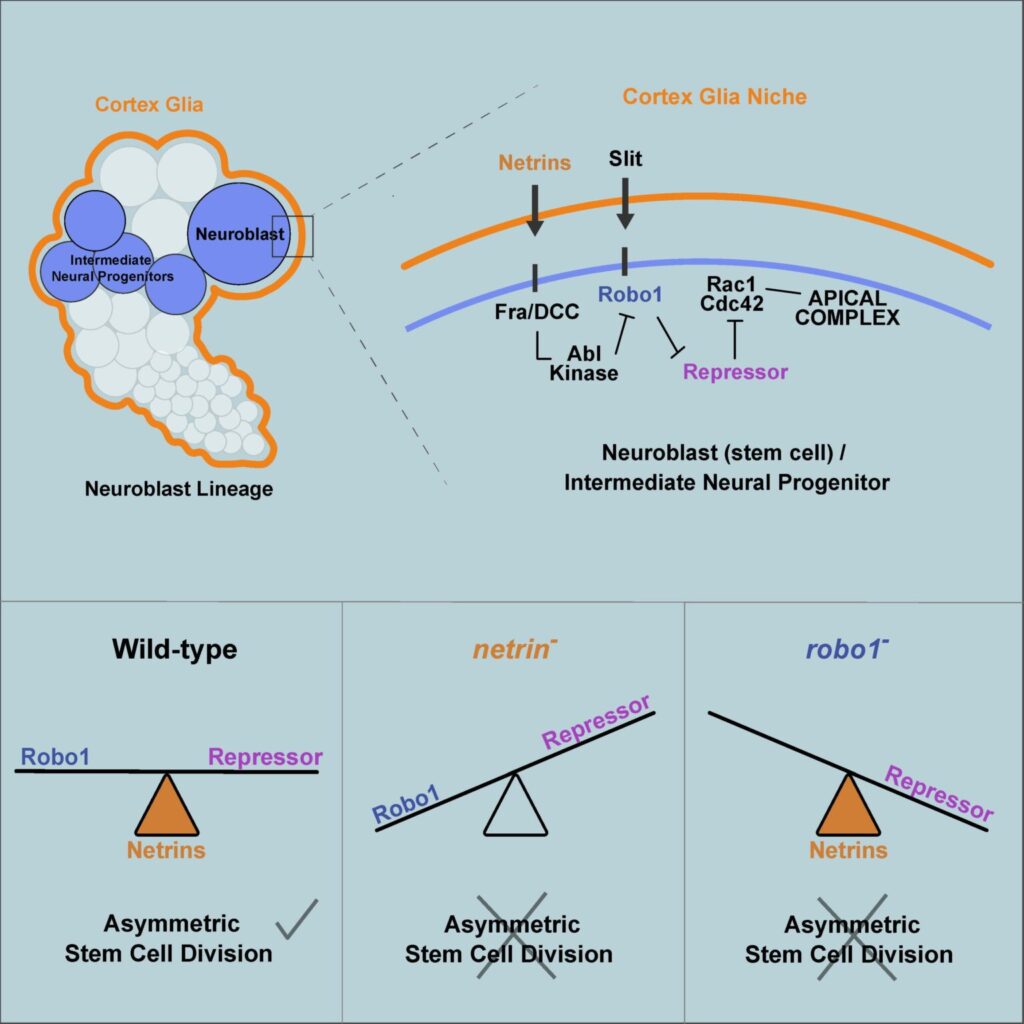
Asymmetric stem cell division (ASCD) is a key mechanism in development, cancer and stem cell biology. Drosophila neural stem cells, called neuroblasts (NBs), divide asymmetrically through intrinsic mechanisms. Here we show that the extrinsic axon guidance cues Netrins, secreted by a glial niche surrounding larval brain neural stem cell lineages, regulate NB ASCD. Netrin-Frazzled/DCC signaling modulates, through Abelson kinase, Robo1 signaling threshold levels in Drosophila larval brain neural stem and progenitor cells of NBII lineages. Unbalanced Robo1 signaling levels induce ectopic NBs and progenitor cells due to failures in the ASCD process. Mechanistically, Robo1 signaling directly impinges on the intrinsic ASCD machinery, such as aPKC, Canoe/Afadin, and Numb, through the small GTPases Rac1 and Cdc42, which are required for the localization in mitotic NBs of Par-6, a Cdc42 physical partner and a core component of the Par (Par-6-aPKC-Par3/Bazooka) apical complex.
Link to the PDF:
de Torres-Jurado et al., Glial-secreted Netrins regulate Robo1/Rac1-Cdc42 signaling threshold levels during Drosophila asymmetric neural stem and progenitor cell division Current Biology (2022)

 Español
Español